Many bots crawl websites that do nothing to generate positive traffic for the site. They just use up available resources and bandwidth of the server. You can reduce this drastically by implementing blocking using ModSecurity to detect the bad agents and then fail2ban to block them in iptables for a period of time. This guide assumes you already have ModSecurity Installed. If you do not, follow our guide to get it installed then proceed with this.
Configure ModSecurity to Block User Agents
In our Apache configuration setup, we already have a include directory for ModSecurity rules
Include /etc/httpd/conf/modsecurity.d/rules/*.conf
So we are going to create a new .conf to start detecting agents
nano /etc/httpd/conf/modsecurity.d/rules/block_user_agents.conf
We are going to add the following and save the file
SecRule REQUEST_HEADERS:User-Agent "@pmFromFile badbots.txt" "id:350001,rev:1,severity:2,log,msg:'BAD BOT - Detected and Blocked. '"
We are then going to create the list of User Agents to be detected and blocked:
nano /etc/httpd/conf/modsecurity.d/rules/badbots.txt
And insert the following user agents. If you want to let some of these in feel free to edit the list as you see fit.
AhrefsBot Anonymizer Attributor Baidu Bandit BatchFTP Bigfoot Black.Hole Bork-edition DataCha0s Deepnet Explorer desktopsmiley DigExt feedfinder gamingharbor heritrix ia_archiver Indy Library Jakarta Java juicyaccess larbin linkdex Missigua MRSPUTNIK Nutch panscient plaNETWORK Snapbot Sogou TinEye TwengaBot Twitturly User-Agent Viewzi WebCapture XX Yandex YebolBot MJ12bot masscan baidu Yandex RSSingBot Scanbot betaBot DotBot SemrushBot mj12bot FeedFetcher seoscanners.net Moreover ltx71 inboundlinks.win sitebot
Configure Fail2Ban
First you will need to install Fail2ban
yum -y install fail2ban
After that has finished installing, you will want to create a new jail file
nano /etc/fail2ban/jail.local
Creating a local jail will allow the main fail2ban configuration to be updated with new updates.
[apache-modsecblock-badbots] enabled = true filter = apache-useragent logpath = /var/log/httpd/error_log action = iptables-multiport[name=apache-badbots, port="http,https", protocol=tcp] postback[name=BADBOT, port="http,https", protocol=tcp] maxretry = 2 bantime = 172800 ignoreip = 127.0.0.0/8 10.0.0.0/8 192.168.1.0/24
Update ignoreip with any local IPs or any others you want to allow in regardless of the UserAgent. This allows each IP to access twice with the a UserAgent indicated in the list, after that it will be banned.
You will then want to create the failregex pattern
nano /etc/fail2ban/filter.d/apache-useragent.conf
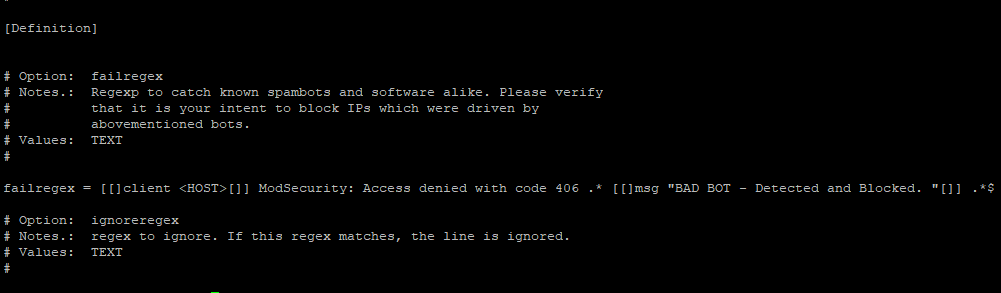
And add the following
# Fail2Ban configuration file # [Definition] # Option: failregex # Notes.: Regexp to catch known spambots and software alike. Please verify # that it is your intent to block IPs which were driven by # abovementioned bots. # Values: TEXT # failregex = [[]client <HOST>[]] ModSecurity: Access denied with code 406 .* [[]msg "BAD BOT - Detected and Blocked. "[]] .*$ # Option: ignoreregex # Notes.: regex to ignore. If this regex matches, the line is ignored. # Values: TEXT #
Go ahead and restart fail2ban and apache
service httpd restart service fail2ban restart
You should now be able to watch the apache error log /var/log/httpd/error.log to see if any bans are picked up.

Hi, very interesting approach – but have not managed to get rid of ahrefs bot so far with this method. Followed your instructions, albeit slightly modified since on Debian. Badbots are detected and written into the error.log alright, but fail2ban fails to pick on them … maybe something wrong with the regex? It looks good to me, but since I am zero on regex I might be overlooking something … Here a sample of what is written into the error.log: [Tue Nov 28 16:34:54.520349 2017] [:error] [pid 30083] [client 51.255.65.33:49402] [client 51.255.65.33] ModSecurity: Warning. Matched phrase “AhrefsBot” at REQUEST_HEADERS:User-Agent. [file… Read more »
Hello Chris,
It might be the format, have tried doing a fail2ban-regex on the jail and log file to confirm its matching the hit through mod security?